If you are searching for “ribosome define,” you are probably looking for a clear, straightforward explanation of what ribosomes are and why they are important. Ribosomes are tiny molecular machines found within all living cells. Their main role is to produce proteins, which are essential for countless biological processes. This article on “ribosome define” will give you an in-depth look at their structure, function, types, and significance in the world of biology.
What Does Ribosome Define Mean in Biology?
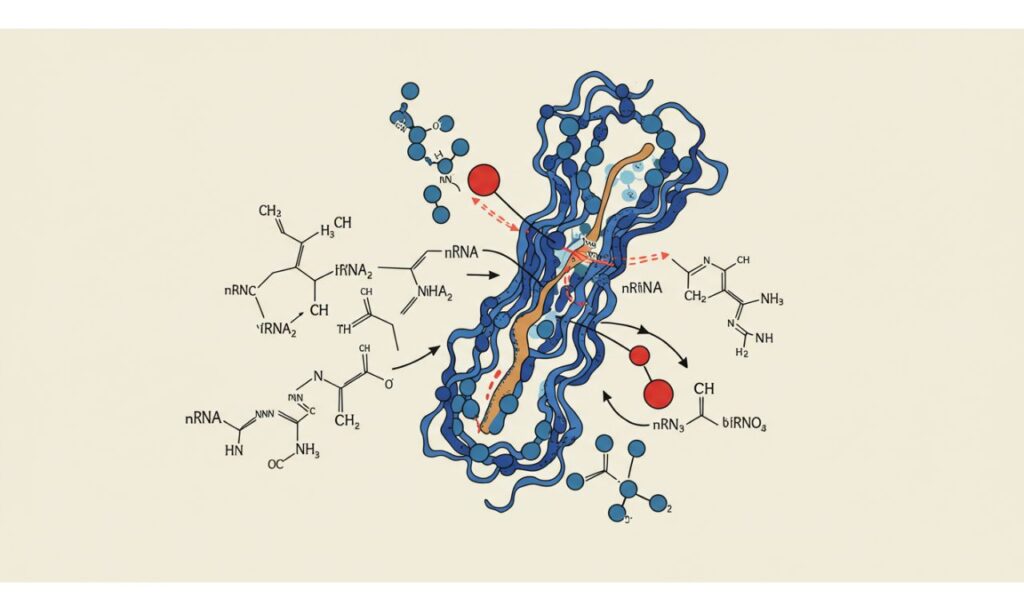
In biological terms, “ribo-some define” refers to the formal explanation of ribo-somes. Ribo-somes are complex particles made of ribos-omal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. They are responsible for translating messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins during the process known as translation. When you explore “ribo-some define,” you learn that they are essential for life, as proteins control most cellular functions.
The Structure of Ribosomes – Ribosome Define in Detail
Ribo-some Define: The Components
When we look at “ribo-some define,” we must understand the two main components:
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): This forms the core of the ribo-some’s structure and catalyzes protein synthesis.
Proteins: These stabilize the rRNA structure and assist in the function of the ribo-some.
Ribosome Define: The Subunits
Ribo-somes are made of two distinct subunits, each with its own rRNA and proteins:
Large Subunit (LSU): This part joins amino acids together to form a polypeptide chain.
Small Subunit (SSU): This reads the mRNA code during translation.
In “ribo-some define,” these subunits are crucial because they work together to translate genetic information into functional proteins.
Where Are Ribosomes Found? – Ribosome Define in Cellular Context
Ribosome Define: In Prokaryotic Cells
In prokaryotic cells like bacteria, ribo-somes float freely in the cytoplasm. They are slightly smaller than those in eukaryotes but serve the same purpose. The ribo-some define in prokaryotes includes the 70S ribosome made of 50S (large subunit) and 30S (small subunit).
Ribosome Define: In Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells, which include plants, animals, fungi, and protists, have larger ribo-somes known as 80S ribo-somes. These consist of a 60S large subunit and a 40S small subunit. In these cells, ribo-somes may be free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), giving the RER its characteristic “rough” appearance.
How Ribosomes Work – Ribosome Define and Protein Synthesis
The core of “ribo-some define” revolves around their role in protein synthesis. This process, known as translation, involves several steps:
Initiation: The small ribo-somal subunit binds to the mRNA.
Elongation: The ribo-some moves along the mRNA, adding amino acids brought by transfer RNA (tRNA).
Termination: When a stop codon is reached, the ribo-some releases the completed protein.
The “ribo-some define” highlights that without ribo–somes, cells could not produce proteins, making life impossible.
Ribosome Define and the Genetic Code
A key aspect of “ribo-some define” is their ability to decode the genetic instructions in mRNA. This decoding allows the ribo-some to link amino acids in the precise sequence dictated by the genetic code. Therefore, ribosomes act as interpreters of genetic information, turning DNA instructions into functional proteins.
Ribosome Define: Types of Ribosomes
Free Ribosomes
These ribo-somes float freely in the cytoplasm and mainly produce proteins that function within the cell itself.
Bound Ribosomes
Attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, bound ribo-somes synthesize proteins destined for export out of the cell or for incorporation into cellular membranes.
Understanding the difference is crucial to the full scope of “ribosome define” because it explains how cells direct protein traffic.
Ribosome Define: The Origin and Evolution of Ribosomes
Scientists believe ribo-somes are among the most ancient molecular machines, dating back billions of years. The concept of “ribo-some define” also involves their evolutionary significance. The structure and function of ribo-somes have remained remarkably conserved, emphasizing their fundamental role in biology.
The Importance of Ribosomes in Medicine – Ribosome Define in Health and Disease
Many antibiotics target bacterial ribo-somes without affecting human ribosomes. This selectivity is due to slight structural differences, an important point in “ribosome define.” For example:
Tetracycline and Erythromycin bind to bacterial ribo-somes to halt protein synthesis, fighting infection.
Additionally, mutations in ribosomal proteins can lead to diseases called ribo-somopathies, which further highlights their biological significance in the “ribosome define” context.
Ribo-some Define in Biotechnology and Research
Ribo-somes are also critical tools in biotechnology. Scientists use ribo-some research for genetic engineering, drug development, and synthetic biology. In this field, “ribo-some define” stretches beyond simple biology, impacting industries like medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.
Conclusion:
When we explore “ribo-some define,” we uncover a molecular powerhouse essential for life. From their structural complexity to their indispensable role in protein synthesis, ribosomes serve as the foundation of biological function. Whether in medicine, evolution, or biotechnology, understanding the ribosome helps unlock the mysteries of life itself.